Do you suffer from heel pain, achilles pain, or have a bunion? Maybe you have a Flatfoot
Flatfoot is more than just an annoyance in buying new shoes, it can be the explanation for chronic heel pain, achilles pain and even that bunion that has been bothering you for a long time. This interview Dr K Kannan from the Specialist Orthpaedic Centre Singapore explains all about the flatfoot.
What is a flatfoot?
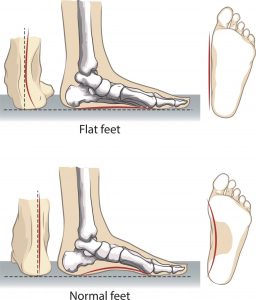
Flat vs Normal Feet
Flat foot is the flatness of the arch of the foot. The concept of flat feet is when you have a broad foot or a splayed foot and when you stand the edge or inner part of the foot collapses or touches the floor. Flat foot is normal and it’s just a shape of the foot.
Conditions of a flatfoot
The problem comes in when there are symptoms related to the flat feet. This can cause problems in children and adults.
Flatfeet with children
Common conditions that might indicate that you have a flat foot in a child are:
- walking funny
- limb length discrepancy – one leg shorter than the other
- curved spine
- shoulder malalignment or dropping
- complain of fatigue after activity or sports
Flatfeet with adult:
Common conditions in adults
- feet pain/aching pain
- deformity
- bunion pain
- presentation of toe deformity
- heel pain or plantar fasciitis
- knee pain – inside or front of knee
- Achilles Tendonitis
- Calf tightness/numbness
- The Evolution of Flat Foot
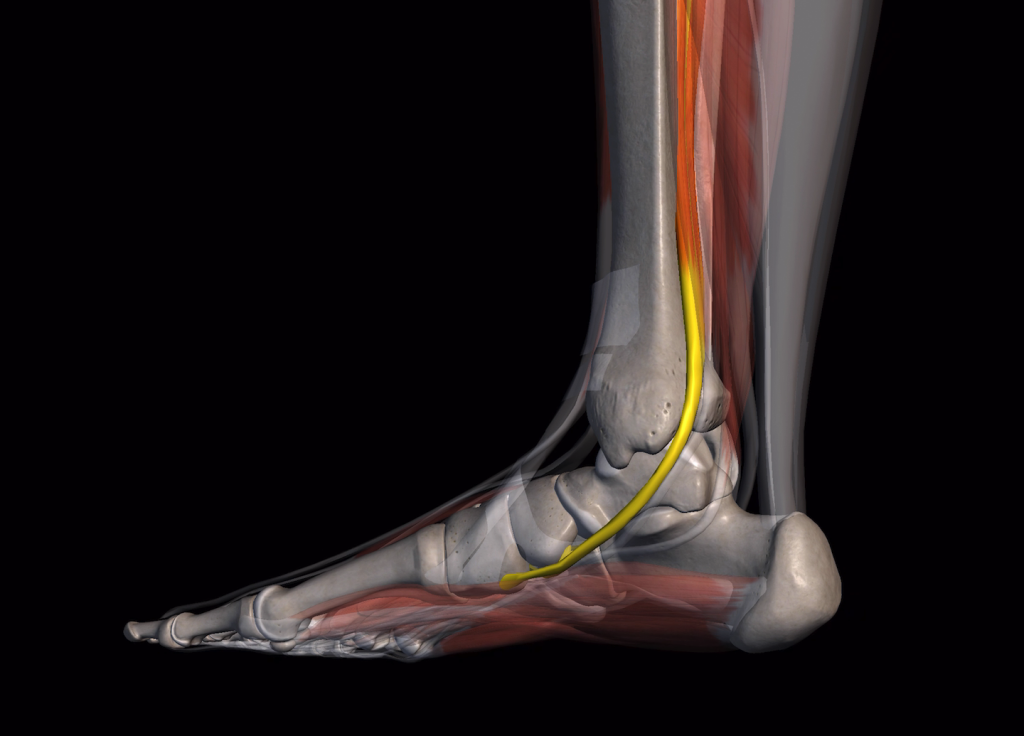
posterior tibial tendon
The anatomy of flat foot includes a very important tendon called the posterior tibial tendon on the inside of the foot. It is this tendon that fails to hold the arch in a curved manner.
Therefore if this tendon starts to fail, the arch starts to collapse overtime. In an adult – it is known as an Adult Flat Foot Deformity (AFFD). In a child, this tendon is still developing, so if the arch of the child is very supple and this tendon does not have the ability to develop in a right way, and if its ignored, in adulthood can develop AFFD.
Investigation and Diagnosis
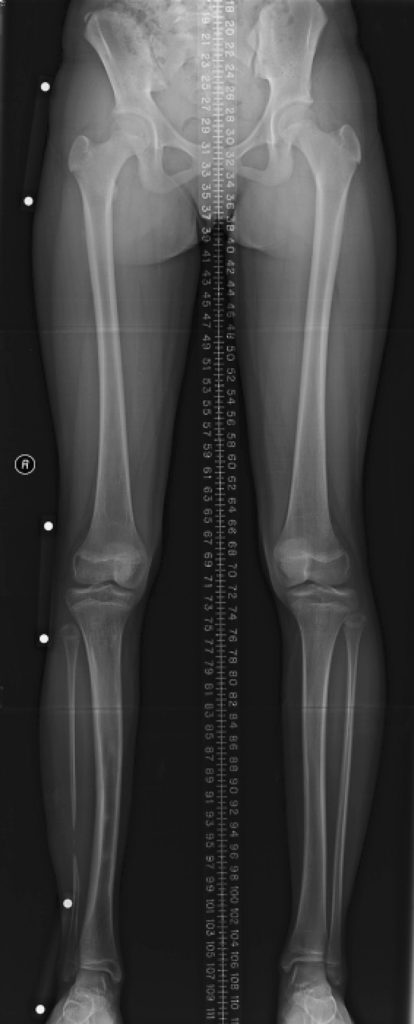
Scanogram
Over 90% of the time, investigation is done through proper history taking and examination of the patient (calf suppleness, alignment and foot). Further investigation through targeted radiological investigations include weight bearing x-ray of the feet and a Scanogram (x-ray taken from the hip, knee and ankle showing alignment and measurements of lower limbs).
Some instances require a x-rays of the spine to check for a pelvic malalignment and an MRI of the ankle.
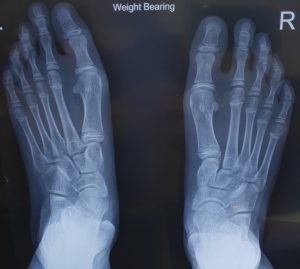
Weight baring X-ray
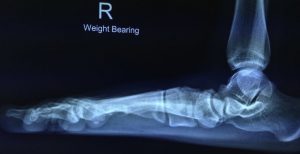
Weight baring X-ray
What a surgery entails.
80-90% cases of flat foot in children doesn’t require surgery as the tissue is still supple. Most of the time, a custom made orthotic is needed to balance gait and re-shape the foot for correct development. If the deformity of the flat foot is quite severe having an impact of their walking or daily activity, a brace maybe the best option. Alternatively, there is a small number of children that may require surgery ranging from simple to complicated procedures.
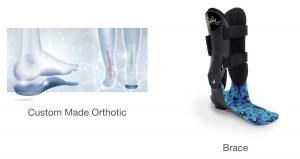
Custom Made Orthotic and Brace
Hypocure Stent
A simple surgery entails putting a small stent into the arch of the foot to raise up the arch, with a 1.5cm minimally invasive incision on the outer part of the ankle under radiological guidance. This is a day surgery done under sedation for half an hour. The patient is given special shoes and is able to walk immediately after the surgery. The wound takes two weeks to heal. With the help of physiotherapy, the patient can get back to into active lifestyle and sports by the end of the month.
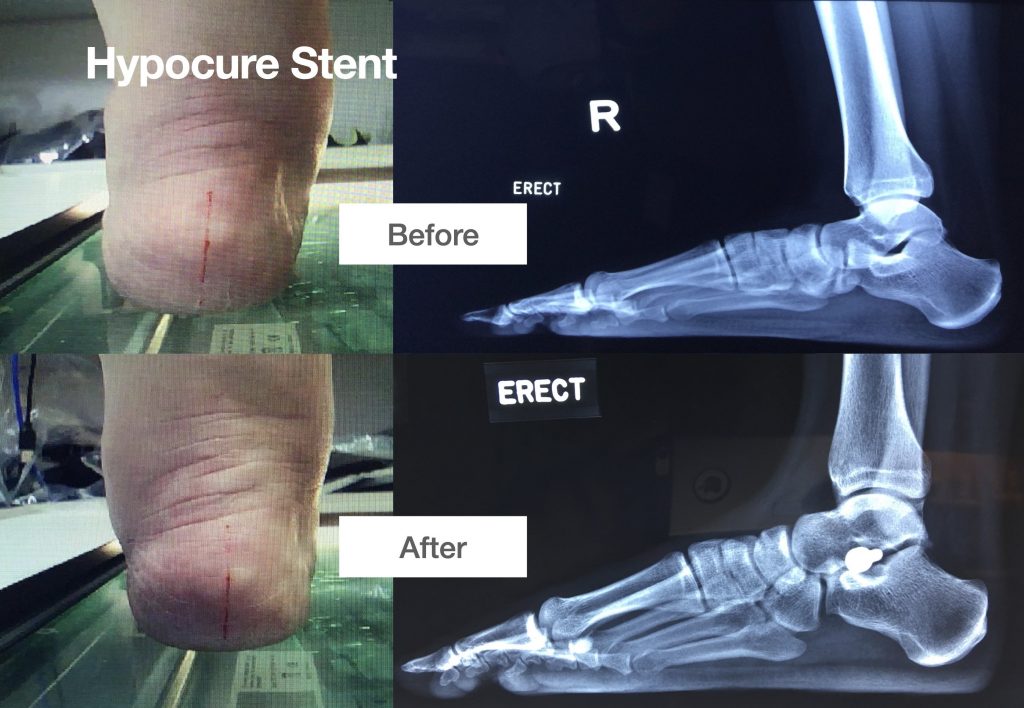
Hypocure Stent
Other Procedures
A more complicated surgery to correct a bad deformity entails a combination of procedures: release of the calf muscle, a stent procedure or an adjunct procedures with plates and screws. The recovery can take 4-6 weeks, where week 1 involves not putting any weight on the feet with the help of a moon boot/aircast boot.
The Bunion
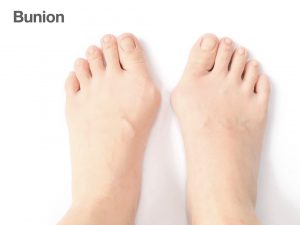
Bunion is one of the consequences of having a flat foot. Bunion surgery entails minimally invasive surgery with 2-2.5cm incision using implants, where patients can walk 2-3 hours after surgery. The recurrence rate following a bunion surgery is nearly 0% – low recurrence, easy acceptability and easy mobility post-surgery.
Post-surgery care
- Wound care – proper dressing and regular change of dressing
- Elevation of leg and icing to avoid swelling
- Post-surgical counselling for specific condition
- Post – surgical rehabilitation – Physiotherapy
Making an appointment
To make an appointment with Dr Kannan, his contact details are
- web: specialistortho.com.sg
- phone: +65 6272 0933
- whatsapp: +65 96288 6933
For Physioactive Singapore, find your closest location at: www.physioactive.sg
For Physioactive Indonesia, book directly online here.








