Hip replacement and non surgical options for chronic hip pain
A hip replacement surgery should be considered carefully, but may be the only solution for your hip pain. Before making this decision there are several other options to consider though. This article based on an interview with Dr Jeffrey Chew Tec Hoc, Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon at the Centre For Orthopaedics, explains exactly what is involved.
The Hip is the part of our body that bears most of the weight and it is located beneath deep layers of strong supporting muscles and ligaments. A healthy hip carries almost 5 times a person’s body weight during everyday activities such as walking.
The hip joint is the junction where the hip joins the leg to the trunk of the body. It comprises two parts: the femur and the acetabulum.
Symptoms of hip pain
Old age and sports injuries are common causes of hip pain.
Predominantly, hip pain manifestations include:
- The anterior aspect of the groin (lower buttock)
- When patients have difficulty rotating their hip internally and externally
- Rising from a sitting position
- The anterior aspect of the knee keeping in mind the nerves between the knees and hip are connected.
- Side of the hip – pain, and clicking
- Aching when going up and down the stairs
Investigation and Diagnosis
Assessment by surgeon includes:
- History taking
- Pain scores
- Note of medication
- Physiotherapy treatment attempts
- Disturbances in daily activities
- Discussion of expectations from the patient and doctor
- Physical Examination – Back, Hip, and Knee
- Range of Motion
- Stiffness
- Examination of gait while walking
- X-rays
- Pelvis
- Specific views of the hip
- Spine
- If required: MRI of the hip and back
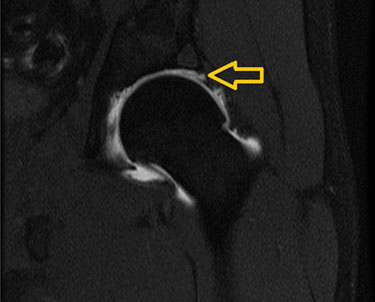
MRI of Labral Tear
Causes of hip pain
Potential causes of hip pain include:
- A loose back
- Labral tear
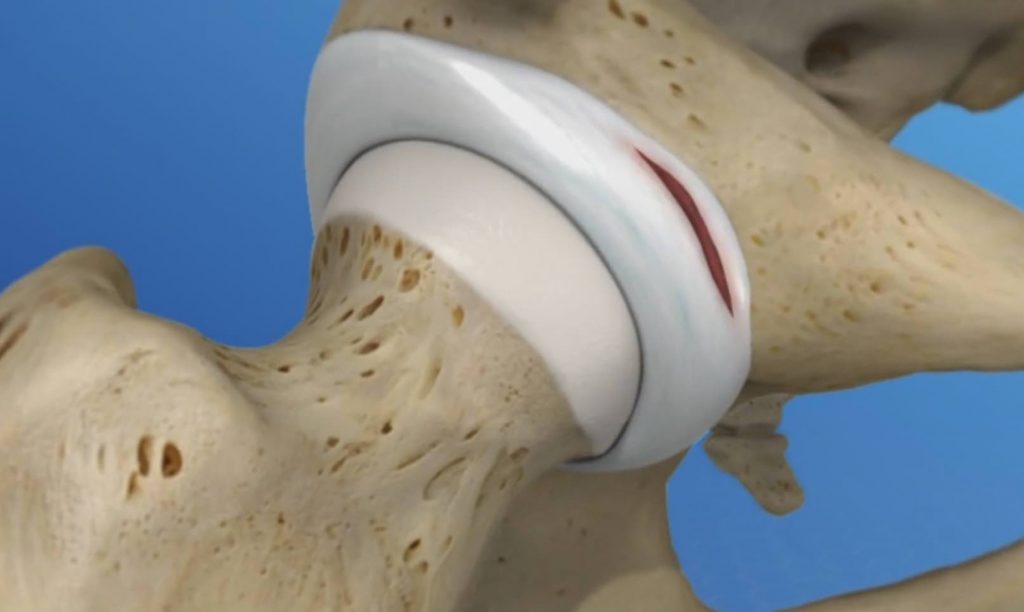
Labral Tear
- The labarum is a piece of rubbery tissue attached to the rim of the hip socket that helps keep the ball of the joint in place. When this cartilage is torn, it is called a labral tear.
- Due to an impingement
- Active people between age 30-40 years old with groin pain
- Progressive arthritis
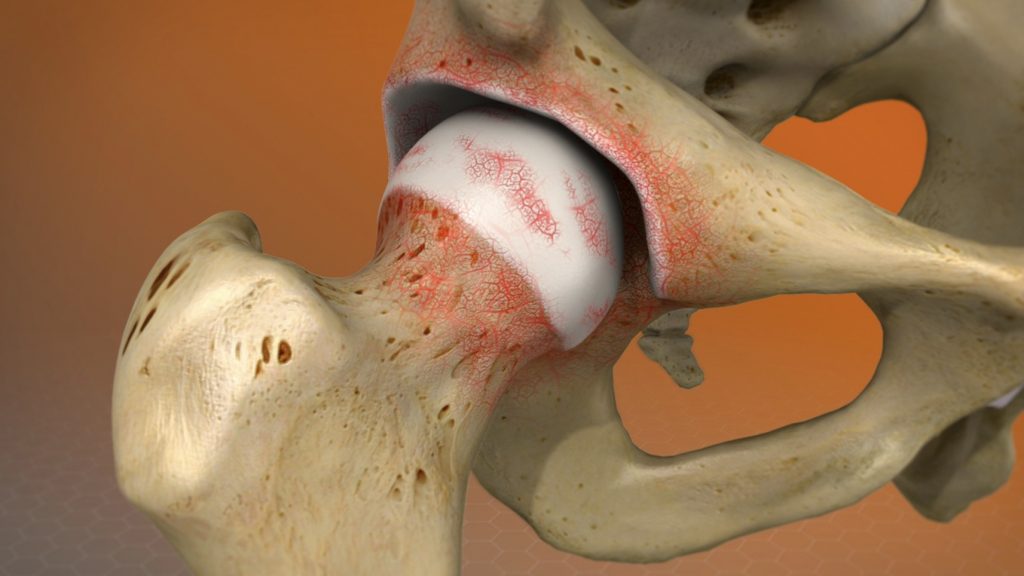
Hip Arthritis
- Caused by wear and tear of cartilage
- Common in elderly patients
- Pain, stiffness, pain at night, loss of range of motion
- Acetabular dysplasia
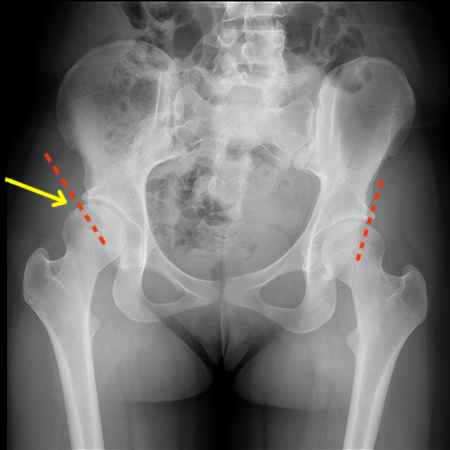
Hip Dysplasia
- Common in women 40-45 years old
Alternative options to surgery
Possible conservative methods before surgery include physiotherapy, medication and injection to the hips.
Injection for the hip
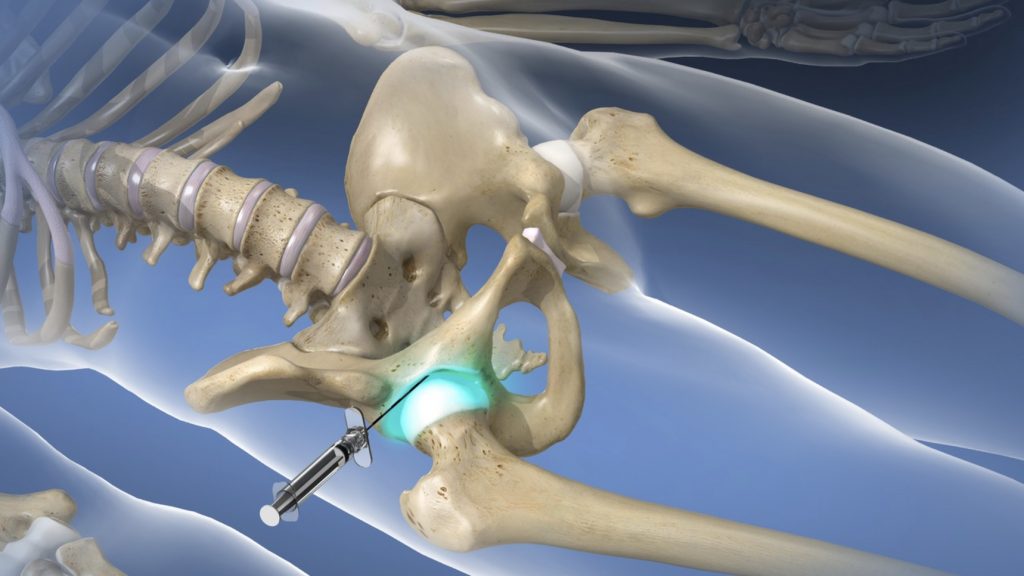
Steroid Injections
- Steroid injection, gel injection, nStride protein injection
- Done with fluoroscopy under X-ray control
- The injection is passed into the hip
- Helps with pain relief
- 2-3 times in a lifetime
- Day surgery
- An alternative for a temporary measure
Hip Replacement Surgery: Choosing the right surgical option
Different kinds of hip surgery are:
Labral Tear
- Hip arthroscopy – reparation of the cartilage
Severe arthritis requires Hip replacement
- Method
- Conventional – replacing the cup and stem
- Challenges
- The correct limb length correct
- The perfect position or component
- Robotics System Surgery – femur and acetabulum are accurately put in a safe zone
- Challenges
- Approach
- Anterior
- Posterior
- Minimally invasive
- 2 incision approach
- Materials
- Ceramic
- Metal
- Metal on plastic
- Polyethylene
- Conventional – replacing the cup and stem
What surgery and post-surgery entails
Surgery and Post-surgery
- Done under general anesthesia for 1-1.5 hours
- Nerve blocks are given post-surgery
- Start walking the day after surgery using a walking frame
- Return home after day 3-4
- Range of motion exercise required through physiotherapy
- Progression from walking frame to walking stick
Potential risks involved in a hip replacement
Risk assessment
- General Anaesthetic risk
- Age and fitness of the patient
- Screening of heart
- Surgical Risk
- Special equipment
- Anti-Baltic powder
- Sanitization
- Technical Errors – Removed by robotics
- Minimal blood loss
- Chances of dislocation
- Limb length discrepancy
Making an appointment
To make an appointment with Dr Jeffrey Chew, his contact details are
- web: www.cfo.com.sg
- phone: +65 6684 5828
For Physioactive Singapore, find your closest location at: www.physioactive.sg
For Physioactive Indonesia, book directly online here.